Experiment Dataviews
While an experiment is running, and any time after it finishes, results are tracked and can be visualized in the ClearML Enterprise WebApp (UI).
In addition to all of ClearML's offerings, ClearML Enterprise keeps track of the Dataviews associated with an experiment, which can be viewed and modified in the WebApp.
Viewing an Experiment's Dataviews
In an experiment's page, go to the DATAVIEWS tab to view all the experiment's Dataview details, including:
- Input data selection and filtering
- ROI mapping (label translation)
- Label enumeration
- On-the-fly data augmentation
- Iteration controls
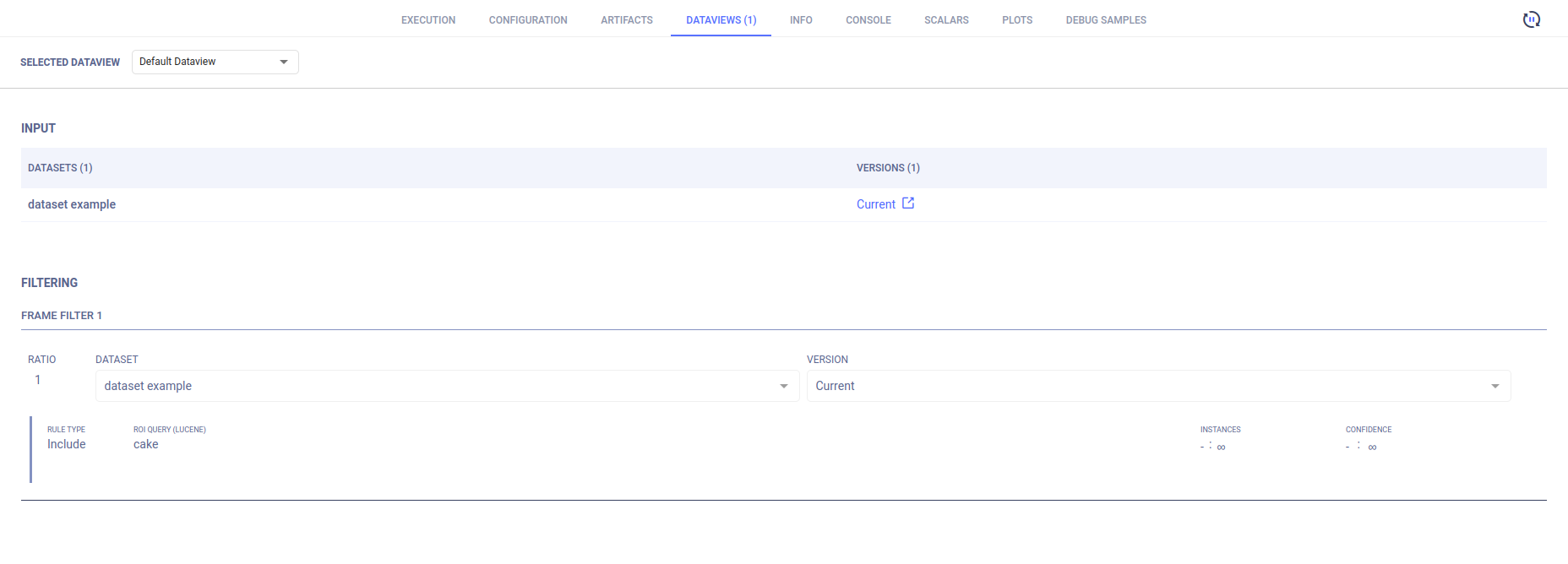
Input
SingleFrames are iterated from the Dataset versions specified in the INPUT area, in the SELECTED DATAVIEW drop-down menu.
Filtering
The FILTERING section lists the SingleFrame filters iterated by a Dataview, applied to the experiment data.
Each frame filter is composed of:
- A Dataset version to input from
- ROI Rules for SingleFrames to include and/or exclude certain criteria.
- Weights for debiasing input data.
Combinations of frame filters can implement complex querying.
For more detailed information, see Filtering.
Mapping
ROI label mapping (label translation) applies to the new model. For example, use ROI label mapping to accomplish the following:
- Combine several labels under another more generic label.
- Consolidate disparate datasets containing different names for the ROI.
- Hide labeled objects from the training process.
For detailed information, see Mapping ROI labels.
Label Enumeration
Assign label enumeration in the LABELS ENUMERATION area.
Augmentation
On-the-fly data augmentation applied to SingleFrames, which does not create new data. Apply data Augmentation in steps, where each step is composed of a method, an operation, and a strength.
For detailed information, see Data augmentation.
Iteration Control
The input data iteration control settings determine the order, number, timing, and reproducibility of the Dataview iterating SingleFrames. Depending upon the combination of iteration control settings, all SingleFrames may not be iterated, and some may repeat.
For detailed information, see Iteration control.