PyTorch Distributed
The pytorch_distributed_example.py
script demonstrates integrating ClearML into a code that uses the PyTorch Distributed Communications Package
(torch.distributed).
The script does the following:
It initializes a main Task and spawns subprocesses, each for an instance of that Task.
The Task in each subprocess trains a neural network over a partitioned dataset (the torchvision built-in MNIST dataset), and reports the following to the main Task:
- Artifacts - A dictionary containing different key-value pairs is uploaded from the Task in each subprocess to the main Task.
- Scalars - Loss reported as a scalar during training in each subprocess Task is logged in the main Task.
- Hyperparameters - Hyperparameters created in each subprocess Task are added to the main Task's hyperparameters.
Each Task in a subprocess references the main Task by calling
Task.current_task(), which always returns the main Task.When the script runs, it creates an experiment named
test torch distributedin theexamplesproject in the ClearML Web UI.
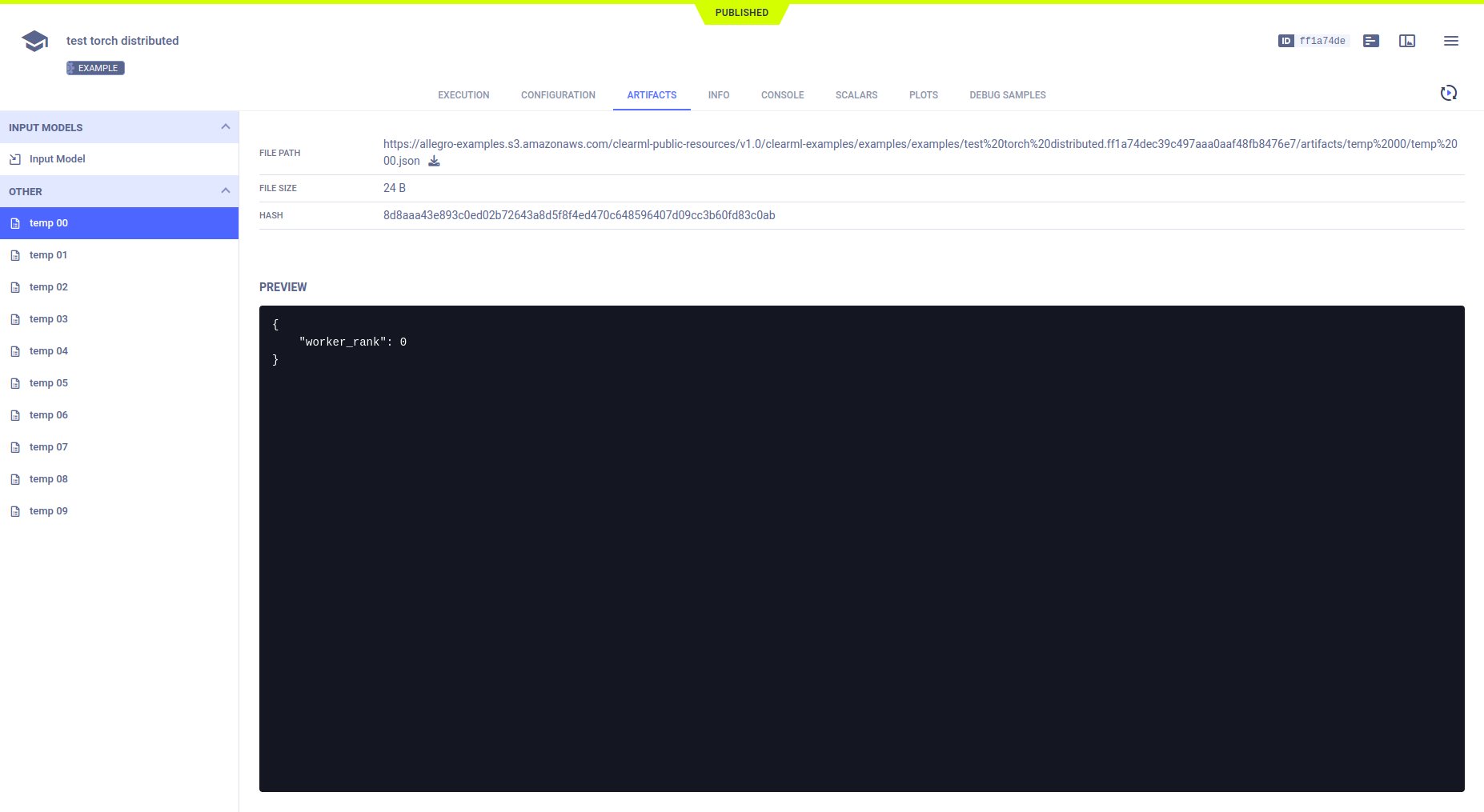
Artifacts
The example uploads a dictionary as an artifact in the main Task by calling Task.upload_artifact()
on Task.current_task (the main Task). The dictionary contains the dist.rank of the subprocess, making each unique.
Task.current_task().upload_artifact(
name='temp {:02d}'.format(dist.get_rank()),
artifact_object={'worker_rank': dist.get_rank()}
)
All of these artifacts appear in the main Task, ARTIFACTS > OTHER.
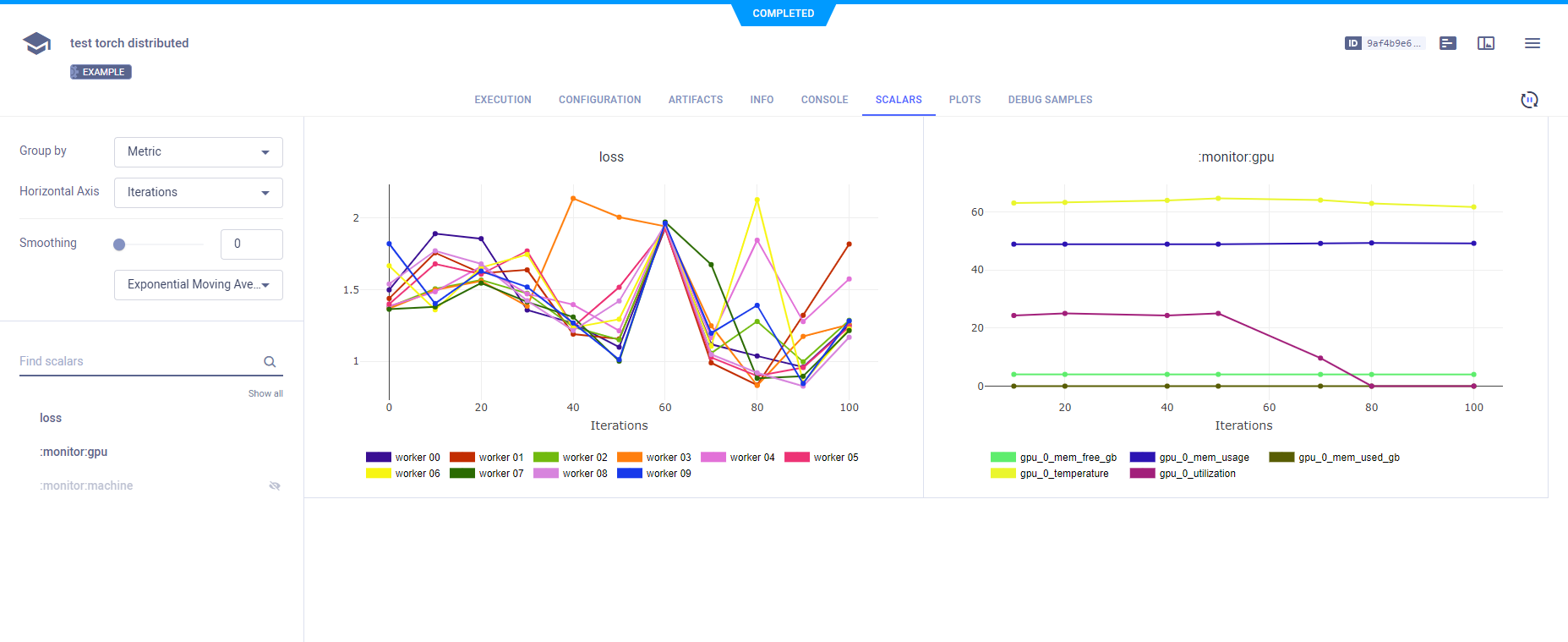
Scalars
Report loss to the main Task by calling Logger.report_scalar()
on Task.current_task().get_logger, which is the logger for the main Task. Since Logger.report_scalar is called with the
same title (loss), but a different series name (containing the subprocess' rank), all loss scalar series are logged together.
Task.current_task().get_logger().report_scalar(
title='loss',
series='worker {:02d}'.format(dist.get_rank()),
value=loss.item(),
iteration=i
)
The single scalar plot for loss appears in SCALARS.
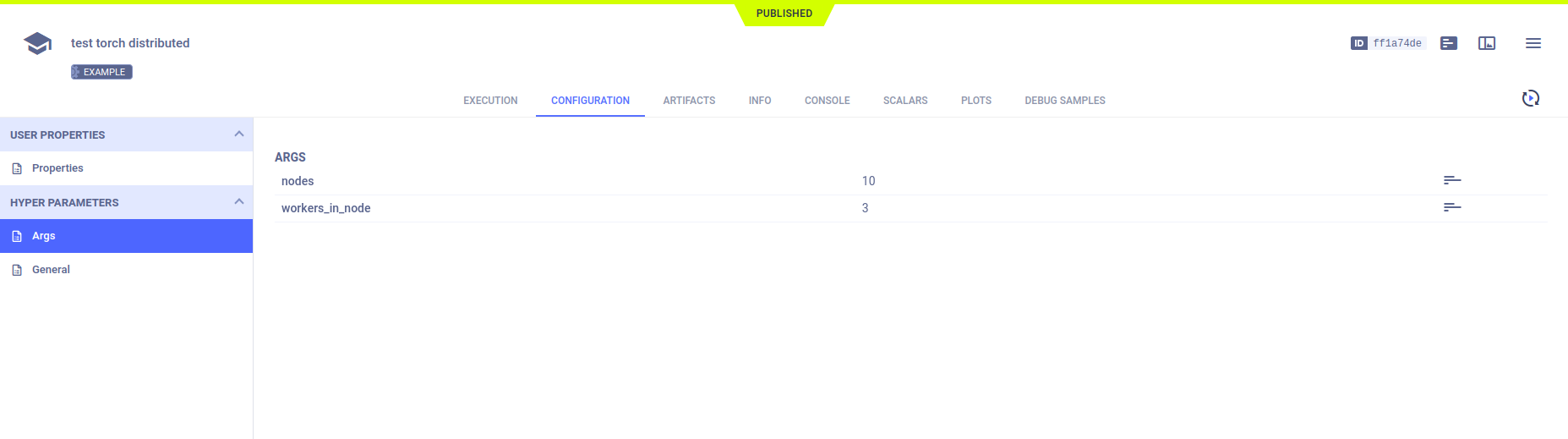
Hyperparameters
ClearML automatically logs the command line options defined using argparse.
A parameter dictionary is logged by connecting it to the Task using Task.connect().
param = {'worker_{}_stuff'.format(dist.get_rank()): 'some stuff ' + str(randint(0, 100))}
Task.current_task().connect(param)
Command line options appear in CONFIGURATION > HYPERPARAMETERS > Args.
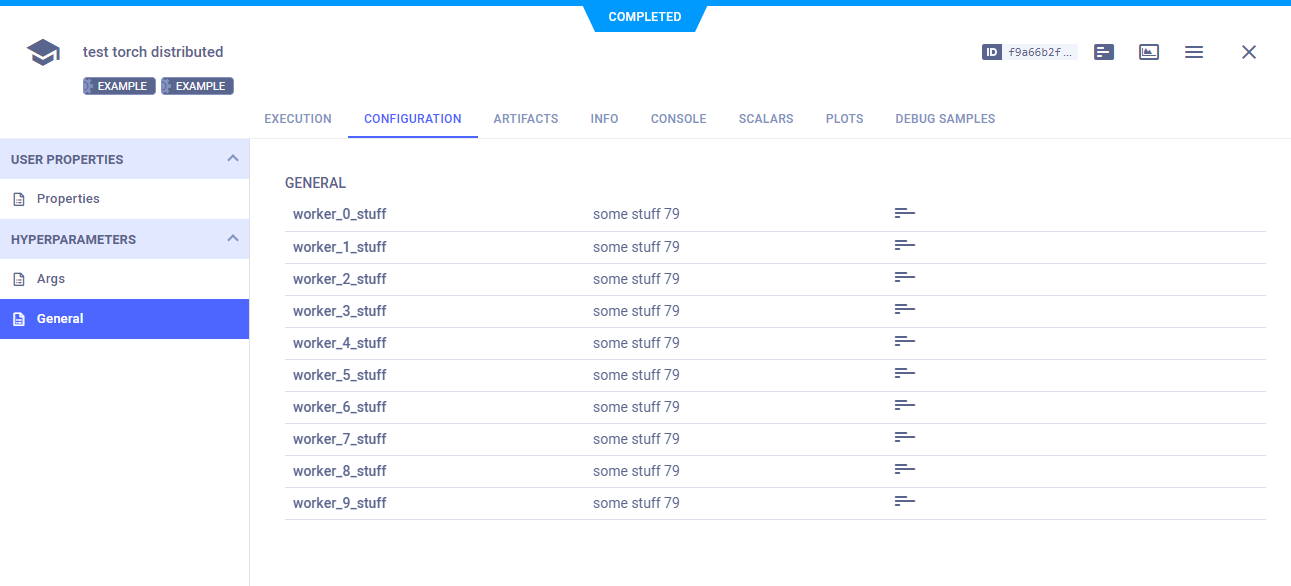
Parameter dictionaries appear in the General section of HYPERPARAMETERS.
param = {'worker_{}_stuff'.format(dist.get_rank()): 'some stuff ' + str(randint(0, 100))}
Task.current_task().connect(param)
Log
Output to the console, including the text messages printed from the main Task object and each subprocess, appears in CONSOLE.